Fred Smith, the Principal of Smith Associates, has more than 30 years of experience in the development, engineering, procurement, construction, project management and overhaul/maintenance of power, cogeneration, and trigeneration plants. Locations have ranged from the Patagonian Desert in Argentina to the Arctic Circle in Canada, and plants have included new and used reciprocating engine, combustion turbine, and steam turbine drivers, packaged cogeneration plants, and hydroelectric plants.
He was involved in installing the first production units of three significant combustion turbine generator models: the Westinghouse W251B12 ECONOPAC GTG, the S&S GE LM6000 GTG, and the Rolls-Royce Trent Econopac GTG, and one of the earlier large Innovative Steam Technologies OTSGs.
Smith has published articles on cogeneration economics, risk management, and privatization in trade magazines and juried journals, made numerous presentations at technical and management conferences, and developed a series of spreadsheet models to effectively evaluate cogeneration economics.

Echo Bay Mines Power Plant Expansion
Echo Bay Mines Lupin gold mine in Canada’s Northwest Territories 95 km south of the Arctic Circle was only accessible by air, or by ice road for ~6 weeks in the winter.
Building steel and two used 3,300 hp GM diesel-fueled recip engines from a BC mine were brought in by ice road and reconditioned at site. Extreme winter weather forced a three month summer construction window for heavy concrete foundations of site-batched concrete and closing-in of the steel building.
The expansion of the power plant provided additional electrical capacity for a new 1,200 hp hoist, and hot water heating for the personnel accommodation at site.
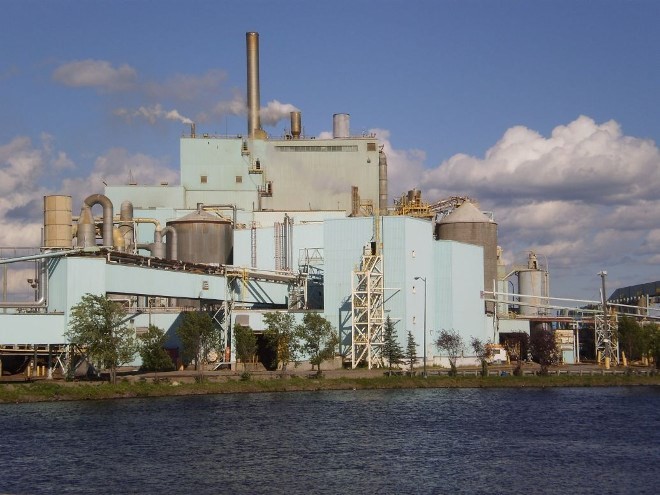

Boise Cascade Pulp and Paper Mill Combined Cycle Cogeneration
New 70 MW combined cycle cogeneration plant at the Boise Cascade Fort Frances pulp and paper mill on the Rainy River in Ontario, Canada.
Congested construction site with heavy lifts by a Manitowoc Ringer crane. Tie-ins to an operating pulp mill. The first production unit of the Westinghouse W251B12 ECONOPAC gas turbine generator (packaged in Hamilton, Ontario), a Foster Wheeler HRSG with duct firing and bypass stack, a Westinghouse STG, and package boiler for backup steam.
Contractual issues with cost-plus and shared saving approach were cited in “Bucking the Trend: Cost-Plus Services in a Lump-Sum Turnkey Market,” Journal of Management in Engineering, ASCE, New York, NY, 1996, by H. Fred Smith.

Ottawa Health Sciences 68 MW Combined Cycle Trigeneration Plant
TransAlta Energy installed the first production unit of the Stewart & Stevenson GE LM6000 aeroderivative gas turbine generator at the Ottawa Health Sciences Centre in Ontario. The Centre includes the Children’s Hospital of Eastern Ontario, Ottawa General Hospital, Ottawa Children’s Treatment Centre, the University of Ottawa, and the Royal Ottawa Health Care Group. The facility also supplies steam to the National Defense Medical Centre and the Rideau Veterans Health Centre. The trigeneration plant includes a 3-pressure Foster Wheeler HRSG with duct burner, a Recoflo short bed demineralization system, an absorption chiller, and an ABB VAX two-speed extraction steam turbine generator.
The plant was Alberta-based TransAlta Energy’s first IPP plant and its first foray into the province of Ontario. It supplied 68 MW of electricity to the provincial grid, and steam, hot water, and chilled water to the members of the Health Sciences Centre.

Atlantic Packaging 58 MW Cogeneration Plant
The Whitby Cogeneration Limited Partnership developed a 58 MW cogeneration plant that used the first production unit of the Rolls-Royce Trent-ECONOPAC gas turbine generator. Gas turbine exhaust gas was directed through an Innovative Steam Technologies (IST) Once Through Heat Recovery Steam Generator (OTSG). High pressure steam was supplied to Atlantic Packaging’s recycled paper products mill in Whitby, Ontario, and electricity was sold to the provincial grid.
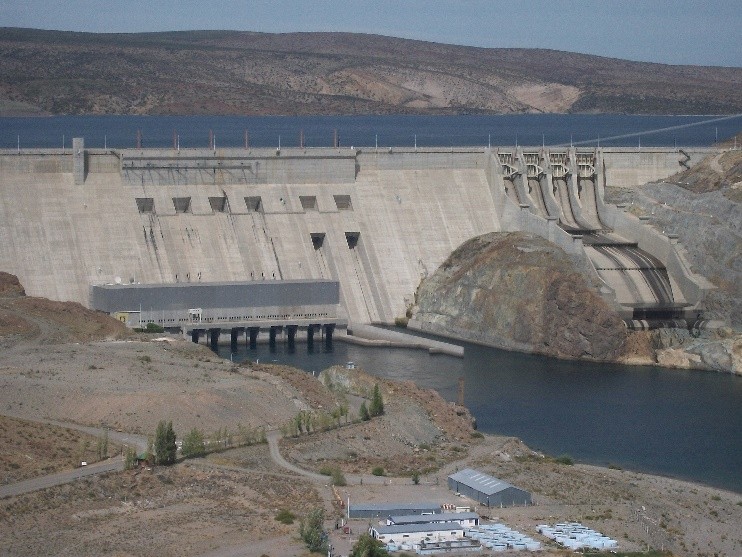

Piedra del Aguila 1400 MW Hydroelectric Plant
Technical and Takeover team leadership for the due diligence evaluation, successful bid preparation and takeover of the 1,400 MW Piedra del Aguila hydroelectric plant in Argentina (Patagonian Desert) as part of an international utility consortium of TransAlta Energy, Duke Energy, and Chilgener S.A. Total installed cost exceeded $1.2 billion. The Piedra del Aguila plant was the largest electrical facility in Argentina and supplied 10% of the country’s electricity. It was part of an extensive privatization of public facilities undertaken by the Argentinian government.
A number of articles were published by Smith regarding the privatization:
“Privatization in Patagonia: the Selling of Argentina’s Largest Hydroelectric Plant,” Proceedings of PMI’94 25th Annual Seminar/Symposium, Vancouver, October 17-20, 1994, Project Management Institute, Newtown Square, PA. 1994. This article is also included in Chapter 3 “Motivating,” Project Management Casebook, Edited by Dr. David I Cleland, University of Pittsburg, et al, PMI Publications, 1997. “Privatizing Works Under Construction – Reining-In the Risks,” Concepts for the Future, US Department of Energy and HCI Publications, Kansas City, MO, 1994 (this chapter was the winner of 1994 HydroVision Award).

Hurricane Hydrocarbons Flare Gas 55 MW Simple Cycle Power Station, Kazakhstan
Hurricane Hydrocarbons, a Canadian oil and gas company, had been directed to reduce flaring in its oilfields in Kumkol, Kazakhstan. Apex Cogen conducted a FEED study and recommended acquisition of used industrial gas turbine generators to consume the flare gas and generate power for Hurricane’s Kumkol oilfields and other grid—connected facilities.
Apex sourced and acquired three packaged GE Frame 5 GTGs in former East Germany, supervised inspection, upgrading, and relocation to Kazakhstan, and provided detailed engineering and installation supervision for the power island, including 10.5 kV to 220 kV substation.
Turbine blade damage was discovered during inspection by Apex Cogen and repaired by the Seller. Upgrades included water injection for NOx reduction, new PLC-based controls system, air filtration system, MCCs.
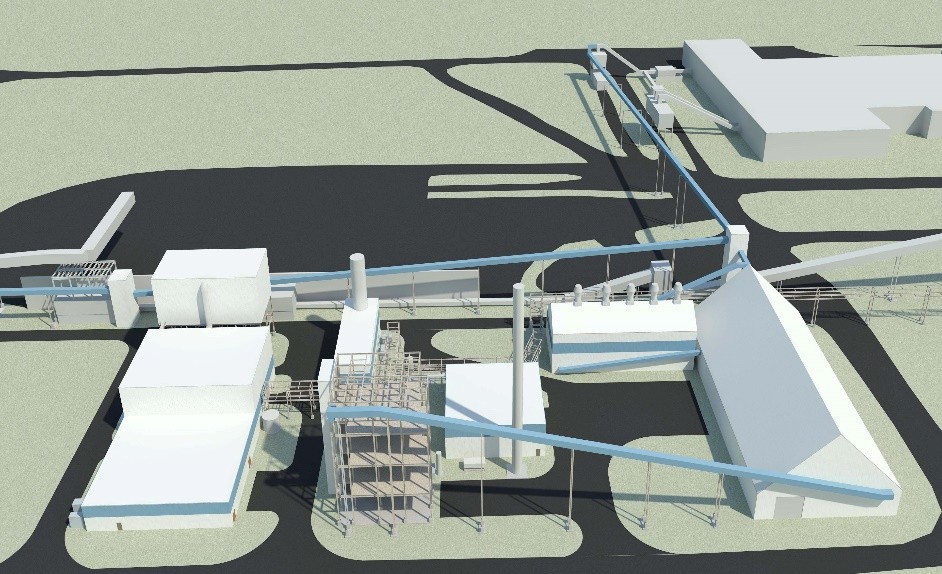
Chickadee Creek Energy Biomass Gasification Plant
Chickadee Creek Energy proposed a new Biomass Gasification and 22 MW combined cycle cogeneration plant for the Millar Western BCTMP mill in Whitecourt, Alberta. The plant would collect, dry, and gasify hog fuel from several sawmill sources, and combust the biomass gas in a 15 MW GTG with steam turbine generator.
FEED and capital cost estimate for the gasification plant including hog fuel storage, drying, and handling, syngas production using the patented Taylor Biomass gasification technology, power production using a modified Solar GTG and condensing extraction STG with cogeneration. TIC=$180 million.

